Governor of Washington
| Washington Governor | |
 | |
| General information | |
| Office Type: | Partisan |
| Office website: | Official Link |
| Compensation: | $187,353 |
| 2024-25 FY Budget: | $70,765,000 |
| Term limits: | None |
| Structure | |
| Length of term: | 4 years |
| Authority: | Washington Constitution, Article III, Section 2 |
| Selection Method: | Elected |
| Current Officeholder | |
Governor of Washington
Jay Inslee | |
| Elections | |
| Next election: | November 5, 2024 |
| Last election: | November 3, 2020 |
| Other Washington Executive Offices | |
| Governor • Lieutenant Governor • Secretary of State • Attorney General • Treasurer • Auditor • Superintendent of Education• • Agriculture Commissioner • Insurance Commissioner• Natural Resources Commissioner• Labor Commissioner• Public Service Commissioner | |
The Governor of the State of Washington is an elected constitutional officer, the head of the executive branch and the highest state office in Washington. The Governor is popularly elected every four years by a plurality and has no term limit.[1]
Washington has a Democratic trifecta. The Democratic Party controls the office of governor and both chambers of the state legislature.
Washington has a Democratic triplex. The Democratic Party controls the offices of governor, secretary of state, and attorney general.
Current officeholder
The 23rd and current governor is Jay Inslee, a Democrat elected in 2012. He succeeded Christine Gregoire (D) on January 16, 2013.[2]
Authority
The Constitution of Washington addresses the office of the governor in Article III, the Executive.
Under Article III, Section 2:
|
The supreme executive power of this state shall be vested in a governor... |
Constitutional provisions
The constitutional duties, rights and responsibilities of the Office of the Governor of the State of Washington are primarily laid out in Article III of the Washington State Constitution. Article III has been amended two times since the constitution was approved in 1889. Two of these amendments are relevant to the governor's prerogatives:
- Washington Amendment 6, Gubernatorial Succession Measure (1910)
- Washington Gubernatorial Vetoes, SJR 140 (1974)
Qualifications
A candidate for governor must be:
- a citizen of the United States
- a qualified elector of the state of Washington
- at least 18 years old[3]
Vacancies
- See also: How gubernatorial vacancies are filled
Details of vacancy appointments are addressed under Article III, Section 10 of the state constitution.
Whenever the sitting Governor dies, resigns, is removed or impeached, or is unable to discharge the office, the duties shall devolve upon the Lieutenant Governor. After the Lieutenant Governor, the order of succession is as follows:
- the Secretary of State
- the Treasurer
- the Auditor
- the Attorney General
- the Superintendent of Public Instruction
- the Commissioner of Public Lands
If a Governor-elect dies, resigns, declines to take the office, or is disqualified, the Lieutenant Governor-elect shall take office as the Governor. If the Governor-elect is only temporarily unable to take the oath, the Lieutenant Governor-elect serves as Acting Governor until the disability is removed. If both the Governor-elect and the Lieutenant Governor-elect are unable to take the oath, the same line of succession listed above applies.
If the Governor dies, resigns, is removed or if the Governor's disability is permanent and more than two years remain in the current term, a special election is held at the next general election, unless the next general election is less than 30 days away, in which case the special election is moved to the following general election.[4]
Duties
The governor is responsible for ensuring that the laws of the state are faithfully executed (§ 5) and is responsible for the safety of the state, as he or she serves as commander-in-chief of the Washington Militia (§ 8).
Additionally, the governor has the power to appoint heads of departments, agencies, and institutions. The governor is also responsible for presenting the state budget.
Other duties and privileges of the office include:
- Requiring written information from any state officer any aspect of her duties and office (§ 5)
- Addressing each session of the legislature on the state of state and making recommendations (§ 6)
- Convening extraordinary sessions of the General Assembly (§ 7)
- Granting pardons (§ 9)
- Remitting fines and forfeitures (§ 11)
- Vetoing bills, subject to a two-thirds legislative override (§ 12)
- Filling vacancies in all offices not otherwise provided for, including making recess appointments (§ 13)[5]
Elections
Washington elects governors in the presidential elections, that is, in leap years. Legally, the gubernatorial inauguration is always set for noon on the second Monday in January following the election.
In the event of a tie between two candidates, a joint session of the legislature shall cast ballots to choose among the two highest vote-getters.
In the event of a contested election, the legislature shall resolve the issue in the manner set out by law.
| State Executives |
|---|
| Current Governors |
| Gubernatorial Elections |
| 2024 • 2023 • 2022 • 2021 • 2020 • 2019 • 2018 • 2017 • 2016 • 2015 • 2014 |
| Current Lt. Governors |
| Lt. Governor Elections |
| 2024 • 2023 • 2022 • 2021 • 2020 • 2019 • 2018 • 2017 • 2016 • 2015 • 2014 |
Term limits
- See also: States with gubernatorial term limits
Washington governors do not face any term limits.
Partisan composition
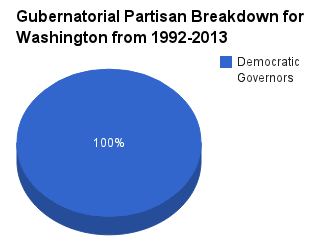
The chart below shows the partisan composition of the Office of the Governor of Washington from 1992 to 2013.
2024
- See also: Washington gubernatorial election, 2024
General election
The primary will occur on August 6, 2024. The general election will occur on November 5, 2024. General election candidates will be added here following the primary.
Nonpartisan primary election
Nonpartisan primary for Governor of Washington
The following candidates are running in the primary for Governor of Washington on August 6, 2024.
Candidate | ||
| Ricky Anthony (D) | ||
| Semi Bird (R) | ||
 | Brian Bogen (No party preference) | |
 | A.L. Brown (R) | |
 | Edward Cale (D) | |
 | Jim Clark (No party preference) | |
| William Combs (Independent) | ||
 | Jeff Curry (Independent) | |
 | Jim Daniel (R) | |
 | Frank Dare (Independent) | |
| Michael DePaula (L) | ||
| Bob Ferguson (D) | ||
| Fred Grant (D) | ||
 | Cassondra Hanson (D) | |
| Bill Hirt (R) | ||
| Jennifer Hoover (R) | ||
| Chaytan Inman (D) | ||
| EL'ona Kearney (D) | ||
| Leon Lawson (Trump Republican Party) | ||
| Alan Makayev (Nonsense Busters Party) | ||
| Rosetta Marshall-Williams (Independence Party) | ||
 | Brad Mjelde (No party preference) | |
| Mark Mullet (D) | ||
| Dave Reichert (R) | ||
| Don Rivers (D) | ||
 | Andre Stackhouse (G) | |
| Alex Tsimerman (Standup-America Party) | ||
 | Martin Wheeler (R) | |
 | Bobbie Samons (No party preference) (Write-in) | |
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Withdrawn or disqualified candidates
- Hilary Franz (D)
- Robert Benjamin Ferguson (D)
- Raul Garcia (R)
- Tim Ford (R)
- Geoff Nelson (Constitution Party)
- Ambra Mason (Constitution Party)
- Tony Tasmaly (R)
- Kriss Schuler (R)
- Eric Nelson (No party preference)
- Reggie Grant (D)
- Laurel Khan (R)
- Daniel Miller (R)
- Robert Arthur Ferguson (D)
2020
- See also: Washington gubernatorial election, 2020
General election
General election for Governor of Washington
Incumbent Jay Inslee defeated Loren Culp in the general election for Governor of Washington on November 3, 2020.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ | Jay Inslee (D) | 56.6 | 2,294,243 | |
| Loren Culp (R) | 43.1 | 1,749,066 | ||
| Other/Write-in votes | 0.3 | 13,145 | ||
| Total votes: 4,056,454 | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Nonpartisan primary election
Nonpartisan primary for Governor of Washington
The following candidates ran in the primary for Governor of Washington on August 4, 2020.
Candidate | % | Votes | ||
| ✔ | Jay Inslee (D) | 50.1 | 1,247,916 | |
| ✔ | Loren Culp (R) | 17.4 | 433,238 | |
| Joshua Freed (R) | 8.9 | 222,553 | ||
| Tim Eyman (R) | 6.4 | 159,495 | ||
| Raul Garcia (R) | 5.4 | 135,045 | ||
| Phil Fortunato (R) | 4.0 | 99,265 | ||
| Don Rivers (D) | 1.0 | 25,601 | ||
| Leon Lawson (Trump Republican Party) | 0.9 | 23,073 | ||
| Liz Hallock (G) | 0.9 | 21,537 | ||
| Cairo D'Almeida (D) | 0.6 | 14,657 | ||
| Anton Sakharov (Trump Republican Party) | 0.6 | 13,935 | ||
| Nate Herzog (Pre-2016 Republican Party) | 0.5 | 11,303 | ||
 | Gene Hart (D) | 0.4 | 10,605 | |
 | Omari Tahir-Garrett (D) | 0.4 | 8,751 | |
 | Ryan Ryals (Unaffiliated) | 0.3 | 6,264 | |
| Henry Dennison (Socialist Workers Party) | 0.2 | 5,970 | ||
| GoodSpaceGuy (Trump Republican Party) | 0.2 | 5,646 | ||
| Richard Carpenter (R) | 0.2 | 4,962 | ||
 | Elaina Gonzalez (Independent) | 0.2 | 4,772 | |
 | Matthew Murray (R) | 0.2 | 4,489 | |
| Thor Amundson (Independent) | 0.1 | 3,638 | ||
| Bill Hirt (R) | 0.1 | 2,854 | ||
 | Martin Wheeler (R) | 0.1 | 2,686 | |
 | Ian Gonzales (R) | 0.1 | 2,537 | |
| Joshua Wolf (New Liberty Party) | 0.1 | 2,315 | ||
| Cregan Newhouse (Unaffiliated) | 0.1 | 2,291 | ||
 | Brian Weed (Unaffiliated) | 0.1 | 2,178 | |
| Alex Tsimerman (Standup-America Party) | 0.1 | 1,721 | ||
 | Tylor Grow (R) | 0.1 | 1,509 | |
| Dylan Nails (Independent) | 0.1 | 1,470 | ||
 | Craig Campbell (Unaffiliated) | 0.0 | 1,178 | |
 | William Miller (American Patriot Party) | 0.0 | 1,148 | |
 | Cameron Vessey (Unaffiliated) | 0.0 | 718 | |
 | Winston Wilkes (Propertarianist Party) | 0.0 | 702 | |
| David Blomstrom (Fifth Republic Party) | 0.0 | 519 | ||
 | David Voltz (Cascadia Labour Party) | 0.0 | 480 | |
| Other/Write-in votes | 0.1 | 1,938 | ||
| Total votes: 2,488,959 | ||||
| If you are a candidate and would like to tell readers and voters more about why they should vote for you, complete the Ballotpedia Candidate Connection Survey. | ||||
Do you want a spreadsheet of this type of data? Contact our sales team. | ||||
Withdrawn or disqualified candidates
- Mathew Mackenzie (R)
- Phillip Bailey (D)
- Asa Palagi (Independent)
- Lisa Thomas (Unaffiliated)
- Matthew Heines (Unaffiliated)
2016
- See also: Washington gubernatorial election, 2016
The general election for governor was held on November 8, 2016.
Incumbent Jay Inslee defeated Bill Bryant in the Washington governor election.
| Washington Governor, 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Vote % | Votes | |
| Democratic | 54.24% | 1,760,520 | ||
| Republican | Bill Bryant | 45.49% | 1,476,346 | |
| Write-in votes | 0.26% | 8,416 | ||
| Total Votes | 3,245,282 | |||
| Source: Washington Secretary of State | ||||
Full history
To view the electoral history dating back to 2000 for the office of Governor of Washington, click [show] to expand the section. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2012Christine Gregoire (D) did not run for re-election in 2012. Jay Inslee (D) narrowly defeated Republican attorney general Rob McKenna in the general election on November 6, 2012.[6]
2008On November 4, 2008, Christine Gregoire won re-election to the office of Governor of Washington. She defeated Dino Rossi in the general election.
2004 On November 2, 2004, Christine Gregoire won election to the office of Governor of Washington. She defeated Dino Rossi, Ruth Bennett in the general election.
2000 On November 7, 2000, Gary Locke won re-election to the office of Governor of Washington. He defeated John Carlson, Steve W. LePage in the general election.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Divisions
Note: Ballotpedia's state executive officials project researches state official websites for information that describes the divisions (if any exist) of a state executive office. That information for the Governor of Washington has not yet been added. After extensive research we were unable to identify any relevant information on state official websites. If you have any additional information about this office for inclusion on this section and/or page, please email us.
State budget
Role in state budget
- See also: Washington state budget and finances
The state operates on a biennial budget cycle. The sequence of key events in the budget process is as follows:[7]
- Budget instructions are sent to state agencies in June.
- State agency budget requests are submitted between August and September.
- The governor submits his or her proposed budget to the Washington State Legislature on or before December 20.
- The legislature adopts a budget between April and June. A simple majority is required to pass a budget.
- The biennial budget cycle begins in July.
Washington is one of 44 states in which the governor has line item veto authority.[7][8]
The governor is required by statute to submit a balanced budget to the legislature. Likewise, the legislature must pass a balanced budget.[7]
Governor's office budget
The budget for the Governor's Office in Fiscal Year 2024-2025 was $70,765,000.[9]
Compensation
The governor's salary is addressed in Article III, Section 14 of the Washington Constitution. The constitution initially set the annual salary of the governor at $4,000 but provided for the amount to be raised to a maximum of $6,000 at the discretion of the Washington State Legislature. Since 1986, the governor's salary is determined by the Washington Citizens' Commission on Salaries for Elected Officials.[10]
In 1948, the voters adopted the 20th constitutional amendment, creating Article 28, Section 1, which authorized the state legislature to establish the compensation received by all elected state officials. Several changes to the procedure, including three more constitutional amendments, followed, the most recent being the 78th amendment or House Joint Resolution 49. Approved voters in the 1986 general election, HJR 49 created the Washington Citizens' Commission on Salaries for Elected Officials, the independent salary-setting authority that took over the legislature's responsibility of setting the salaries of elected officials across the three branches of the Washington state government.[11]
2022
In 2022, the officer's salary was $187,353, according to the Council of State Governments.[12]
2021
In 2021, the governor received a salary of $187,353, according to the Council of State Governments.[13]
2020
In 2020, the governor’s salary was increased to $182,179, according to the Council of State Governments.[14]
2019
In 2019, the governor’s salary was increased to $183,072, according to the Council of State Governments.[15]
2018
In 2018, the governor’s salary was increased to $175,353, according to the Council of State Governments.[16]
2017
In 2017, the governor’s salary was increased to $173,617, according to the Council of State Governments.[17]
2016
In 2016, the governor’s salary was increased to $171,898, according to the Council of State Governments.[18]
2015
In 2015, the governor received a salary of $166,891, according to the Council of State Governments. [19]
2014
In 2014, the governor received a salary of $166,891, according to the Council of State Governments.[20]
2013
In 2013, the governor's salary remained at $166,891.[21]
2012
In 2012, the governor was paid an estimated $166,891 according to the Council of State Governments.
Historical officeholders
There have been 23 governors of Washington since 1889. Of the 23 officeholders, 12 were Republican, 10 were Democrats, and one was a Populist/Democrat.[22]
| List of Former Officeholders from 1889-Present | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Name | Tenure | Party | ||
| 1 | Elisha Peyre Ferry | 1889 - 1893 | |||
| 2 | John Harte McGraw | 1893 - 1897 | |||
| 3 | John Rankin Rogers | 1897 - 1901 | Populist, Democrat | ||
| 4 | Henry McBride | 1901 - 1905 | |||
| 5 | Albert E. Mead | 1905 - 1909 | |||
| 6 | Samuel G. Cosgrove | 1909 - 1909 | |||
| 7 | Marion E. Hay | 1909 - 1913 | |||
| 8 | Ernest Lister | 1913 - 1919 | |||
| 9 | Louis Folwell Hart | 1919 - 1925 | |||
| 10 | Roland H. Hartley | 1925 - 1933 | |||
| 11 | Clarence Daniel Martin | 1933 - 1941 | |||
| 12 | Arthur B. Langlie | 1941 - 1945 | |||
| 13 | Monrad Charles Wallgren | 1945 - 1949 | |||
| 14 | Arthur B. Langlie | 1949 – 1957 | |||
| 15 | Albert Dean Rosellini | 1957 - 1965 | |||
| 16 | Daniel Jackson Evans | 1965 - 1977 | |||
| 17 | Dixy Lee Ray | 1977 - 1981 | |||
| 18 | John Dennis Spellman | 1981 - 1985 | |||
| 19 | Booth Gardner | 1985 - 1993 | |||
| 20 | Michael Lowry | 1993 - 1997 | |||
| 21 | Gary Locke | 1997 - 2005 | |||
| 22 | Chris Gregoire | 2005 - 2013 | |||
| 23 | Jay Inslee | 2013 – present | |||
History
Partisan balance 1992-2013
Throughout every year from 1992-2013 there were Democratic governors in office for Washington. Washington is one of seven states that were run by a Democratic governor for more than 80 percent of the years between 1992-2013.
Across the country, there were 493 years of Democratic governors (44.82%) and 586 years of Republican governors (53.27%) from 1992 to 2013.
Over the course of the 22-year study, state governments became increasingly more partisan. At the outset of the study period (1992), 18 of the 49 states with partisan legislatures had single-party trifectas and 31 states had divided governments. In 2013, only 13 states had divided governments, while single-party trifectas held sway in 36 states, the most in the 22 years studied.
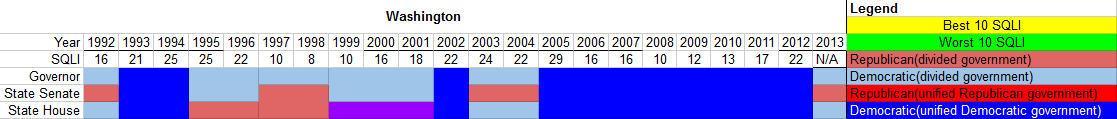
The chart below shows the partisan composition of the Office of the Governor of Washington, the Washington State Senate and the Washington House of Representatives from 1992 to 2013.
SQLI and partisanship
The chart below depicts the partisanship of the Washington state government and the state's SQLI ranking for the years studied. For the SQLI, the states were ranked from 1-50, with 1 being the best and 50 the worst. During the course of the study, Washington had a number of Democratic trifectas. The state experienced both high and low rankings during the years with Democratic trifectas. Its highest ranking overall, finishing 8th, occurred in 1998 during a divided government.
State profile
| Demographic data for Washington | ||
|---|---|---|
| Washington | U.S. | |
| Total population: | 7,160,290 | 316,515,021 |
| Land area (sq mi): | 66,456 | 3,531,905 |
| Race and ethnicity** | ||
| White: | 77.8% | 73.6% |
| Black/African American: | 3.6% | 12.6% |
| Asian: | 7.7% | 5.1% |
| Native American: | 1.3% | 0.8% |
| Pacific Islander: | 0.6% | 0.2% |
| Two or more: | 5.2% | 3% |
| Hispanic/Latino: | 12% | 17.1% |
| Education | ||
| High school graduation rate: | 90.4% | 86.7% |
| College graduation rate: | 32.9% | 29.8% |
| Income | ||
| Median household income: | $61,062 | $53,889 |
| Persons below poverty level: | 14.4% | 11.3% |
| Source: U.S. Census Bureau, "American Community Survey" (5-year estimates 2010-2015) Click here for more information on the 2020 census and here for more on its impact on the redistricting process in Washington. **Note: Percentages for race and ethnicity may add up to more than 100 percent because respondents may report more than one race and the Hispanic/Latino ethnicity may be selected in conjunction with any race. Read more about race and ethnicity in the census here. | ||
Presidential voting pattern
- See also: Presidential voting trends in Washington
Washington voted for the Democratic candidate in all six presidential elections between 2000 and 2020.
Pivot Counties (2016)
Ballotpedia identified 206 counties that voted for Donald Trump (R) in 2016 after voting for Barack Obama (D) in 2008 and 2012. Collectively, Trump won these Pivot Counties by more than 580,000 votes. Of these 206 counties, five are located in Washington, accounting for 2.43 percent of the total pivot counties.[23]
Pivot Counties (2020)
In 2020, Ballotpedia re-examined the 206 Pivot Counties to view their voting patterns following that year's presidential election. Ballotpedia defined those won by Trump won as Retained Pivot Counties and those won by Joe Biden (D) as Boomerang Pivot Counties. Nationwide, there were 181 Retained Pivot Counties and 25 Boomerang Pivot Counties. Washington had four Retained Pivot Counties and one Boomerang Pivot County, accounting for 2.21 and 4.00 percent of all Retained and Boomerang Pivot Counties, respectively.
More Washington coverage on Ballotpedia
- Elections in Washington
- United States congressional delegations from Washington
- Public policy in Washington
- Influencers in Washington
- Washington fact checks
- More...
Contact information
Office of the Governor
PO Box 40002
Olympia, WA 98504-0002
Phone: 360-902-4111
Fax: 360-753-4110
See also
| Washington | State Executive Elections | News and Analysis |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
External links
Footnotes
- ↑ Washington Legislature, "Constitution of the State of Washington, Section III," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Governor Jay Inslee, "About Jay," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Legislature, "Constitution of the State of Washington, Section III," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Legislature, "Constitution of the State of Washington, Section III," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Legislature, "Constitution of the State of Washington, Section III," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Secretary of State, "August 7, 2012 Primary Results: State executives," accessed August 8, 2012
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Budget Processes in the States, Spring 2021," accessed January 24, 2023
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "Separation of Powers: Executive Veto Powers," accessed January 26, 2024
- ↑ Washington State Legislature, "Engrossed Substitute Senate Bill 5187," December 6, 2023
- ↑ Washington Citizens' Commission on Salaries for Elected Officials, "Homepage," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Washington Citizens' Commission on Salaries for Elected Officials, "Homepage," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Book of the States 2022 Table 4.11: Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries," provided to Ballotpedia by CSG personnel
- ↑ Issuu, "The Book of the States 2021," accessed September 28, 2022
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2020," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2019," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2018," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2017," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2016," accessed August 27, 2016
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries, 2015," accessed August 27, 2016
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "Selected State Administrative Officials: Annual Salaries," accessed December 8, 2014
- ↑ Council of State Governments, "CSG Releases 2013 Governor Salaries," June 25, 2013
- ↑ National Governors Association, " Former governors of Washington," accessed January 14, 2021
- ↑ The raw data for this study was provided by Dave Leip of Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections.
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||
State of Washington Olympia (capital) | |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2024 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |